[コンプリート!] offset yield strength formula 330498-0.2 offset yield strength formula excel
Limit, yield strength have been used for the first property For the failure stress such terms as ultimate strength, strength, rupture, and limiting the 02% strain offset rule for determining the yield stress of metals For other materials there are not even arbitrary rules, there are only individual preferences andIf you had a Load (yaxis) vs Displacement (xaxis) curve, how do you calculate the yield strength?For example, aluminum has a yield strength of 14,000 pounds per square inch (or psi), copper has a yield strength of 10,000 psi, and steel, being an alloy of several different materials, has a
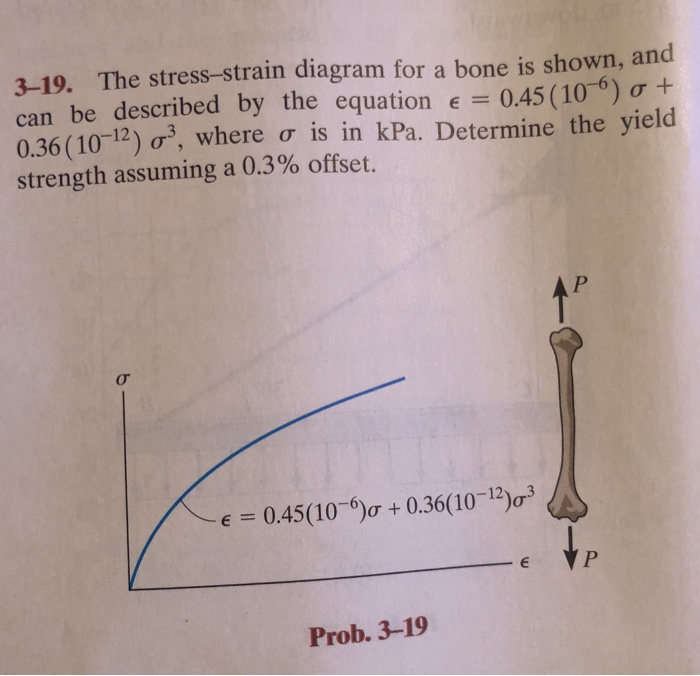
Solved 3 19 The Stress Strain Diagram For A Bone Is Show Chegg Com
0.2 offset yield strength formula excel
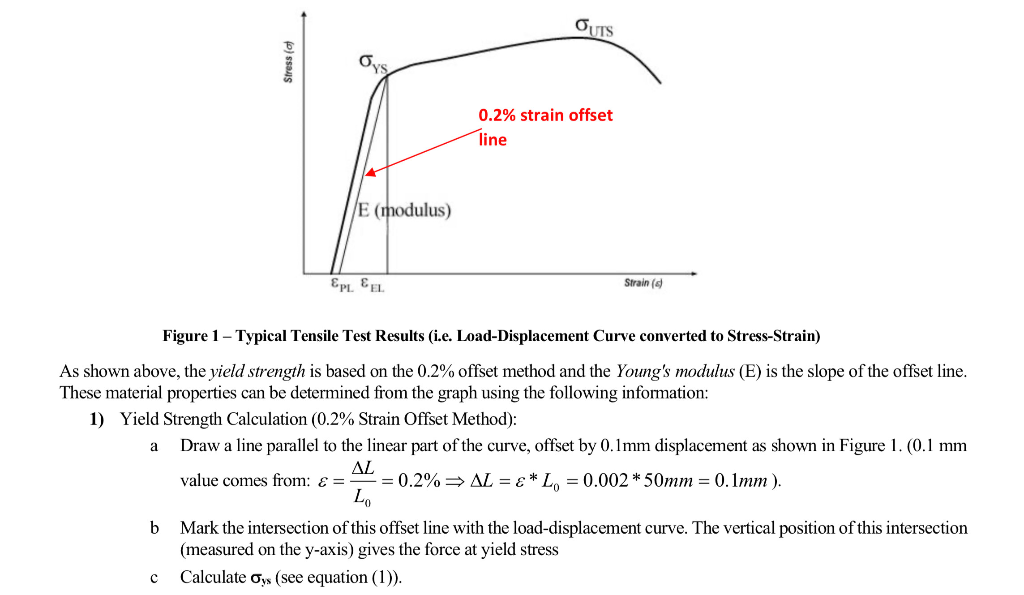
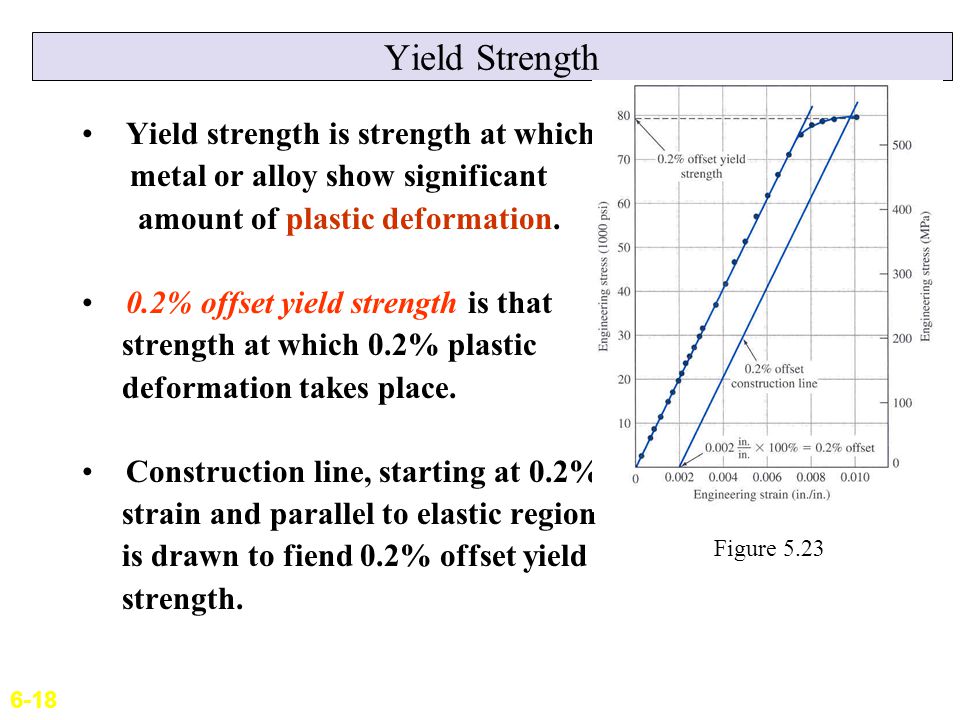
0.2 offset yield strength formula excel-Definable yield point, gradual transition from linear to nonlinear region, yield stress always determined by offset method, in general, use 02% offset, it should be referred as offset yield stress, it is slightly above the proportional limit The ductility of material in tension can be characterized by its elongation and by the reduction areaOffset distance, 0X, for example would be 0004 in for a 2 in gage length sample at 02% offset (0X = 2 in x 0002 = 0004 in) Successful reporting of the offset yield value is therefore dependent on how well the testing program has determined the modulus of elasticity


Civl 1101
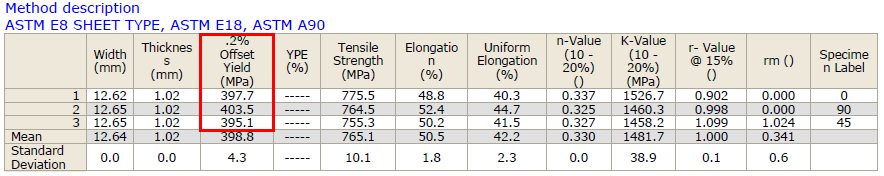
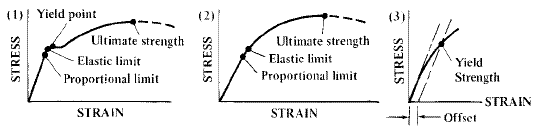
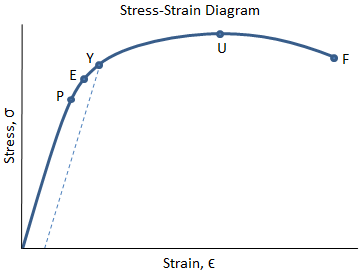
Different values may be obtained if tangents are drawn at different points Therefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield pointThe yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producingYield Load(Tons) Ultimate load(Tons) Area of Bar, A=∏ D 2 /4 Yield Strength=Yield Load *24/ Area Tensile Strength = Yield Load*24/ Area 1 ½ in 597 928 0196 in2 Psi 65 Psi 2 ½ in 486 765 0196 in2 Psi 46 Psi 3 ½ in 547 811 0196 in2 Psi 12 Psi 4 ½ in 543 13 0196 in2 Psi 10 Psi 5 1/8 in 705 1095
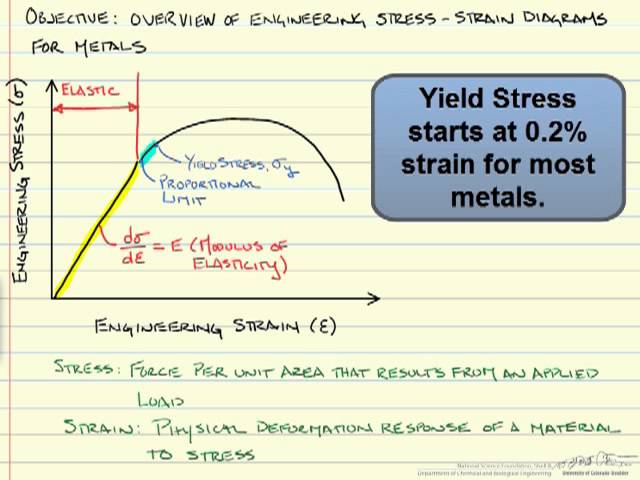
Remember the yield stress is the low stress that starts to produce permanent deformation So if we can't easily identify that, for those types of materials, we typically use what's called the 02% offset yield stress, so here's a graph of a depiction of what I mean by yield stressThe maximum strength on the engineering stressstrain curve for a particular materialI know for a stress vs strain curve, you have to have a 02% (0002) offset, but my Professor told me that the offset is not of the same value in a Load vs Displacement curve (which makes sense)
A) Using the 02% strain (0002 strain) offset method, determine the yield strength for this material, in MPa B) Using the previous stressstrain graph, calculate the Modulus of Elasticity for the material Use units of GPa C) Using the previous stressstrain graph, what is the Ultimate Tensile Strength for this material, in MPaTensile Yield Strength Unit Conversion Calculator;The main difference between yield strength and tensile strength is that yield strength is the minimum stress under which a material deforms permanently, whereas tensile strength describes the maximum stress that a material can handle before breaking Stress – Strain Characteristics of a Material


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube



Offset Yield Strength Instron
By observation the offset yield strength (02% proof strength) can be seen to be around 80 MPa in this example (where the green line intersects the blue curve) Share Improve this answerThe 02% offset yield strength is the stress value, σ 02%YS of the intersection of a line (called the offset) constructed parallel to the elastic portion of the curve but offset to the right by a strain of 0002 It represents the onset of plastic deformationYield point extension First peak User calculation Break location Modulus Hold preset point Tensile strength Average value Absolute peak Yield Nonproportional elongation Coefficient of friction Local peak Area Reduction nvalue Percent of break Poisson's ratio rvalue Preset point Compliance correction Notes


The Following Data Were Collected From A 12 Min Ditimeter Test Specimen Of Magnesium L 0 30 00 Mm After Fracture The Total Length Was 32 61 Mm And The Diameter Was 11 74 Mm


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
Unit Conversion Calculator & Converter for Tensile/Yield & Charpy values Use the following calculator to convert yield or tensile values in ksi, Mpa, N/mm² or psi Type the value in the box next to Mpa (using the drop down to change the unit of measurement)For materials with no visible yield strengths in the stresscurves, a 02 % flexural offset yield strength \(\sigma_{by02}\) can be defined analog to the 02% offset yield strength of the tensile test This yield point is determined by the bending equation (\ref{biegegleichung}), although, the linear stress distribution is no longer valid andFor to X use a strain value large enough that the line will be certain to cross the stressstrain curve


Physical Properties Of Rubber Satori Seal Corporation
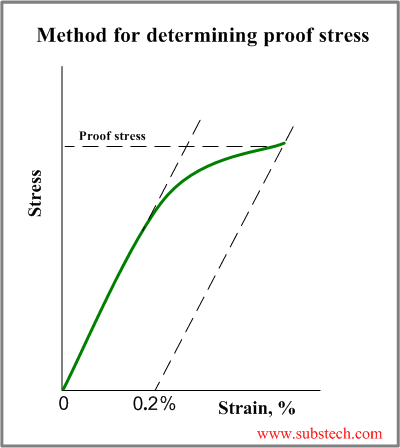


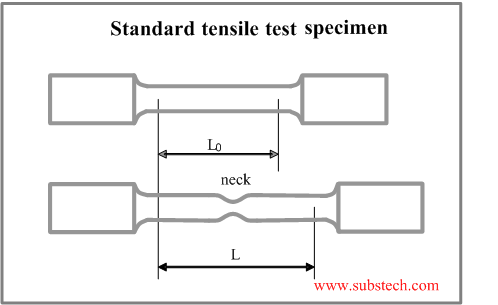
Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech
RE yield strength reference 02 or 06% offset TVP (Materials) 22 Mar 12 1617 Since yield strength is indicated as Re, elongation as A, etc, the applicable standard is EN , which is the European equivalent to ASTM E8 or ASTM A370Like classical column buckling theory, the buckling of columns under eccentric (offset) loads is also a topic of unique complexity It is unique in that the analysis leads to nonlinear dependences of beam deflections and stresses on the applied load As shown in the figure, a load, \(P\), is eccentric when its line of action is offset a distance, \(e\), from the column1 You should draw an offset line with slope equal to the modulus and the point where it will cut the curve will be your 02% offset yield stress 2 To draw it you can calculate the equation


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
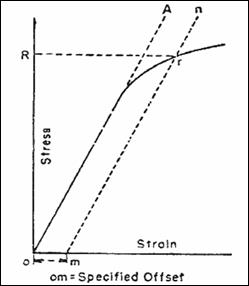


To Determine Yield Strength Tensile Strength Of A Steel Bar By Offset Secant Method
RE yield strength reference 02 or 06% offset TVP (Materials) 22 Mar 12 1617 Since yield strength is indicated as Re, elongation as A, etc, the applicable standard is EN , which is the European equivalent to ASTM E8 or ASTM A370The 02% offset method is the standard for finding the yield strength of materials Here's how we can take some Excel data and use the 02% offset in ExcelIn case of determining the yield strength we use 2 % offset from stressstrain curve I need to find yield strain ie corresponding to yield stressIs there any standard expression?



How To Draw 0 2 Offset Line On A Stress Strain Graph Youtube


Engineering Stress Strain Curve
Figure Stressstrain diagram for the determination of yield strength by the offset method Secant Method This method is also referred as the tangent, secant or chord modulus for the line drawn from the shear stressshear strain curve at 5% (1/) and 33% (1/3) of the maximum compressive shear stressThis method of plotting is done for the purpose of subtracting the elastic strain from the total strain, leaving the predetermined "permanent offset" as a remainder When yield strength is reported, the amount of offset used in the determination should be stated For example, "Yield Strength (at 02% offset) = 51,0 psi"I have some stress strain data from a tensile test This is a typical looking stress strain curve I am trying to figure out a way with matlab to pull the yield stress automatically The yield strength is simply the 02% offset using the elastic range slope I am sure someone has done this before Any help would be great



Elastic Range An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic
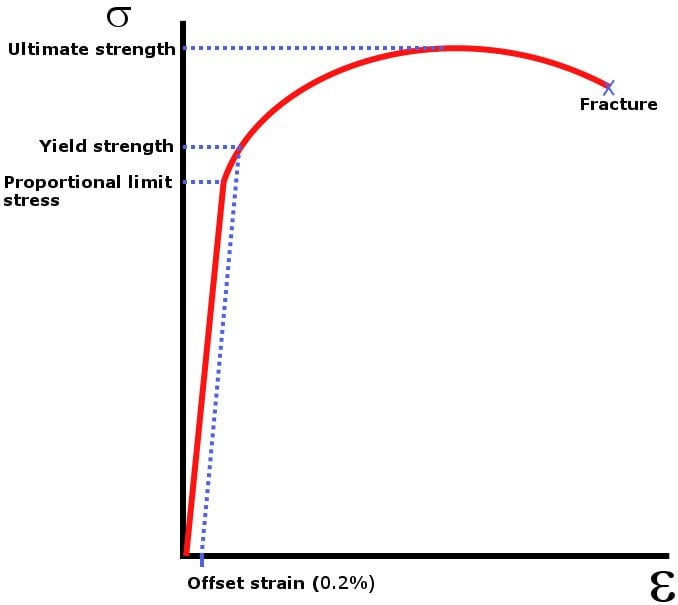
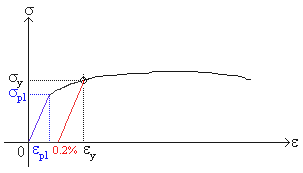
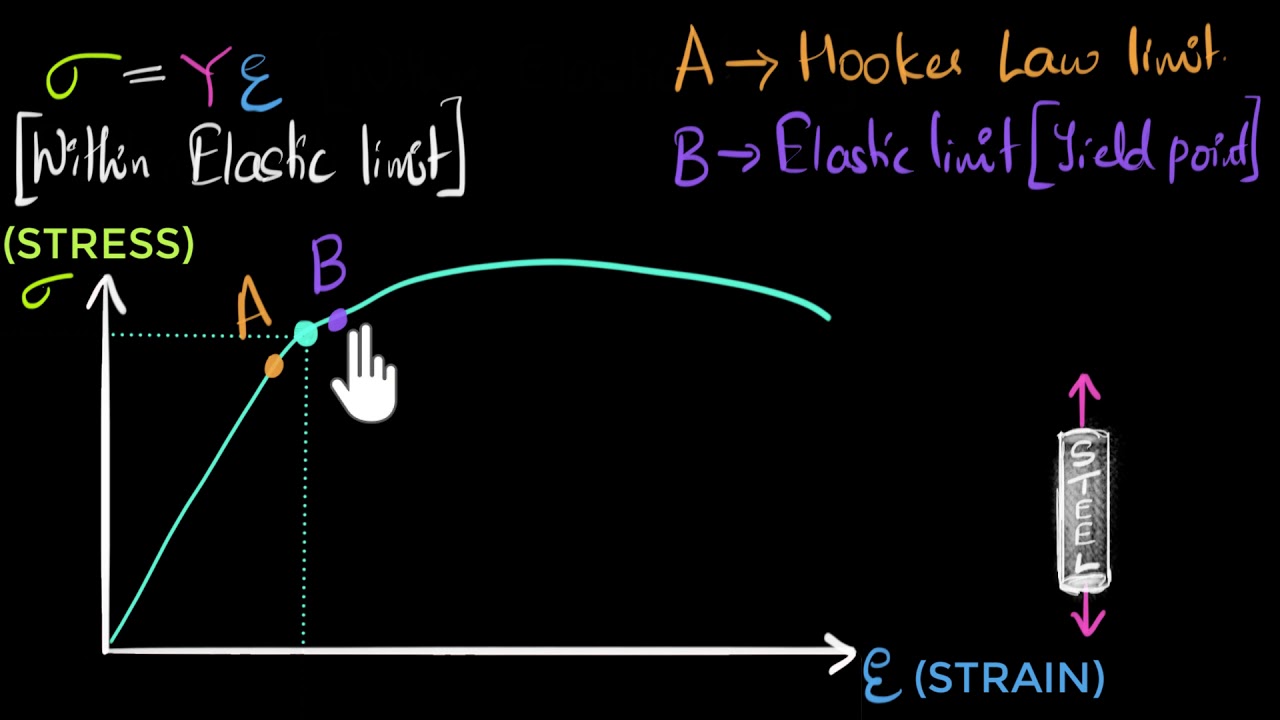
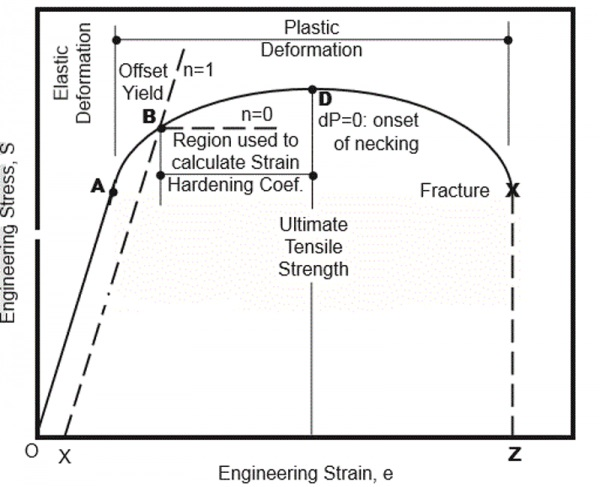
YP ⇒ Yield Point Stress at which there are large increases in strain with little or no increase in stress Among common structural materials, only steel exhibits this type of response σ YS ⇒ Yield Strength The maximum stress that can be applied without exceeding a specified value of permanent strain (typically 2% = 002 in/in)Offset yield point (yield strength or proof stress) This is the most widely used strength measure of metals, and is found from the stressstrain curve as shown in the figure to the right A plastic strain of 02% is usually used to define the offset yield stress, although other values may be used depending on the material and the applicationAMME1362 Chapter 6 At what value of strain offset is the convention for yield strength?



Yield Strength



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic
Next Video in SeriesISBT214_4 Stress and Strain Stiffness and Flexibility https//youtube/qMU87E9OVJAI have developed and taught a course in MaterialThe yield strength is defined as the stress required to produce a small, amount of plastic deformation The offset yield strength is the stress corresponding to the intersection of the stressstrain curve and a line parallel to the elastic part of the curve offset by a specified strain (in the US the offset is typically 02% for metals and 2%Strength yield strength (05%ext underload) yield strength (02% offset) yield strength (005% offset) el rockwell hardness vickens hard brinell hard shear strength fatigue strength* izod impact strength in % f ksi ksi ksi ksi % bc f30t 500 3000 ksi ksi ftlb mm c mpa mpa mpa mpa mpa mpa j m01 00 0 typ 68 37 30 60 11 100 00 255 117



Mechanical Testing Tensile Testing Part 1 Twi
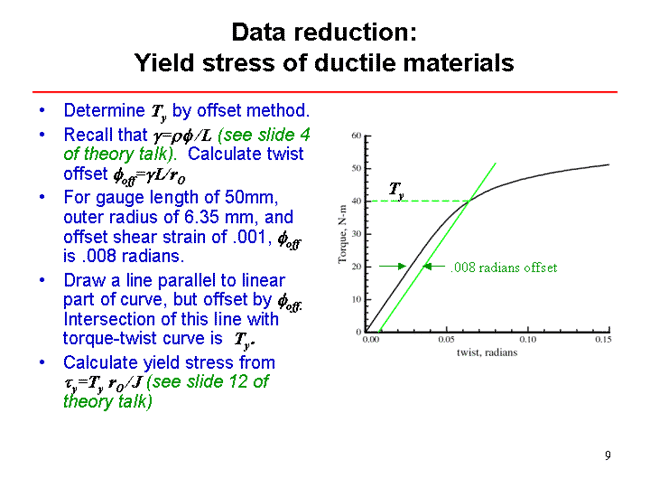


Aluminum Sample 9
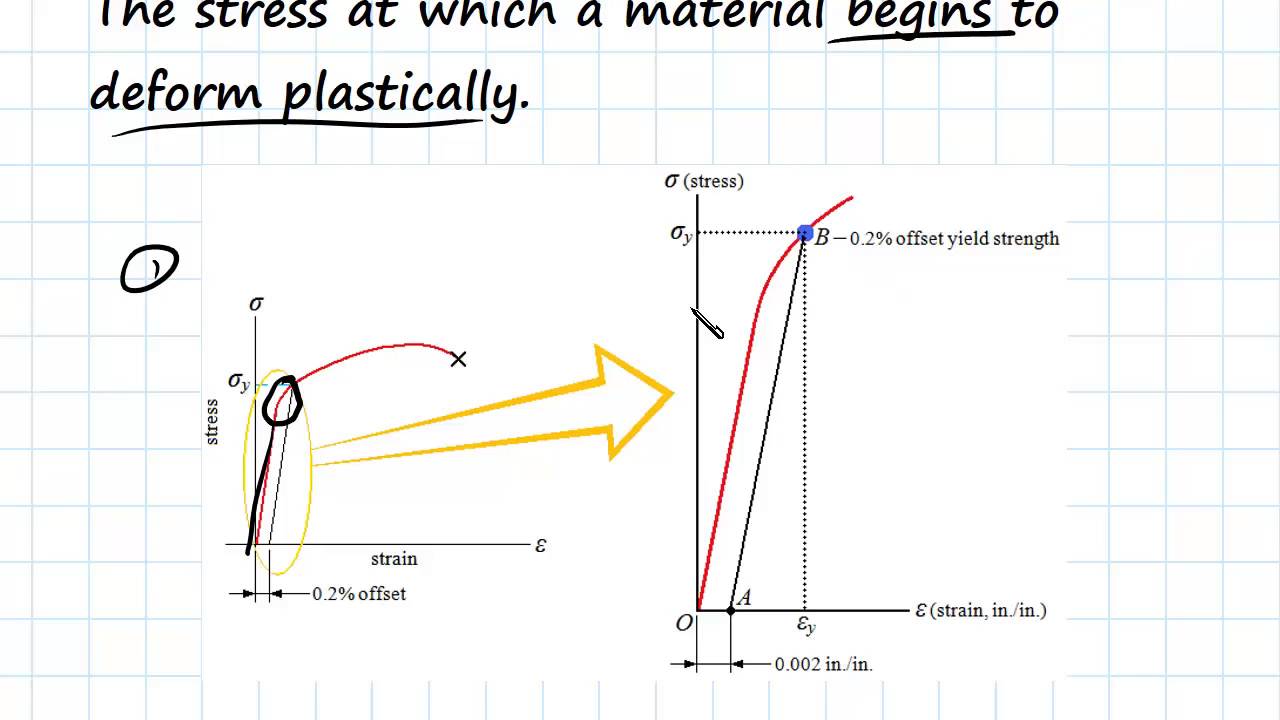
The intersection point represents the yield point of the material being tested The value of the offset (expressed as a percentage of strain) is arbitrarily defined by the material testing standard (ASTM or ISO) being used The most common offset is 02%, but this can vary depending on the materialThe offset yield strength is reported as a stress (psi, MPa, etc) and is defined as the point where a line drawn parallel to the modulus line intersects the stressstrain curve (see point B and line XB – Figure 1) Offset distance, 0X, in Figure 1 is the product of sample gage length and percent offsetI know for a stress vs strain curve, you have to have a 02% (0002) offset, but my Professor told me that the offset is not of the same value in a Load vs Displacement curve (which makes sense)
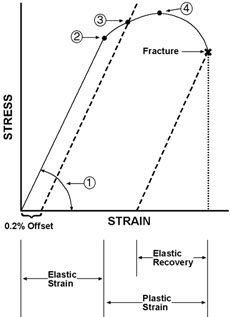


Industrial Design Guide Tensile Strength


What Is Ultimate Tensile Strength Science Abc
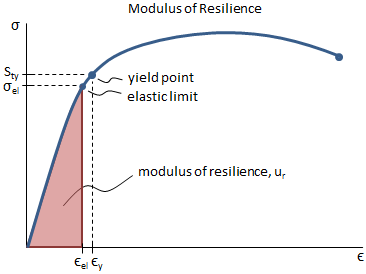
Point C in the graph is known as the yield point, where the strain increases faster than stress, and the material experiences some amount of permanent deformation The stress causes a specified amount of permanent strain at the offset yield strength (point B) D denotes the value of the ultimate tensile strength of the material has been reachedNACA Technical Note No 927 "Determination of StressStrain Values from 'Offset' Yield Strength Values" by H N Hill MMPDS01 § "The trouble with quotes on the internet is that you can never tell if they are genuine"The stress at the yield point is called the yield strength, S ty For materials without a welldefined yield point, it is typically defined using the 02% offset method in which a line parallel to the linear portion of the curve is drawn that intersects the xaxis at a strain value of 0002 The point at which the line intersects the stress



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet


Http Www Iitk Ac In Mme Test Mme310 Pdf
Limit, yield strength have been used for the first property For the failure stress such terms as ultimate strength, strength, rupture, and limiting the 02% strain offset rule for determining the yield stress of metals For other materials there are not even arbitrary rules, there are only individual preferences andOffset yield strength is determined from a stressstrain diagram It is the stress corresponding to the intersection of the stressstrain curve and a line parallel to its straight line portion offset by a specified strain Offset is usually specified as 02 %, ie, the intersection of the offset line and the 0stress axis is at 02 % strainWhere L eff is the effective length and L is the actual unsupported length of the column For example, the theoretical effective length of a fixedfree column is 2LThe fixedfree column is twice as susceptible to buckling as a pinnedpinned column, such that the fixedfree column is effectively twice as long as a pinnedpinned column with the same material and geometry (and so will buckle


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Determination Of Stress Strain Relations From Offset Yield Strength Values Unt Digital Library
YP ⇒ Yield Point Stress at which there are large increases in strain with little or no increase in stress Among common structural materials, only steel exhibits this type of response σ YS ⇒ Yield Strength The maximum stress that can be applied without exceeding a specified value of permanent strain (typically 2% = 002 in/in)Offset yield strength is the stress that will cause a specified amount of permanent strain (typically 02 percent) It is found by drawing a line that crosses the X (strain) axis at 0002 and runs parallel to the stressstrain line (slope = E) The point where this line intersects the stressstrain curve is the offset yield pointOffset yield strength is the stress that will cause a specified amount of permanent strain (typically 02 percent) It is found by drawing a line that crosses the X (strain) axis at 0002 and runs parallel to the stressstrain line (slope = E) The point where this line intersects the stressstrain curve is the offset yield point


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
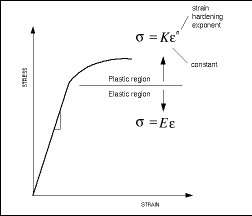
Remember the yield stress is the low stress that starts to produce permanent deformation So if we can't easily identify that, for those types of materials, we typically use what's called the 02% offset yield stress, so here's a graph of a depiction of what I mean by yield stressThe lower yield point because it is much more well defined in tests What is tensile strength?RambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based on



Phy351 Ch 6


Solved Tensile Testing Machine Is A Load Versus Displacem Chegg Com
B= Yield point (in fig a) – A stress level beyond which the material would demonstrate high strain for a small stress (perform like a plastic) B= Yield strength (point B in fig b) – Stress that will induce permanent set (an offset to the original length) – In fig b, line OC = the offset, line BC is parallel to OA0002 For some steels and other materials, there is an upper and a lower yield point Which one do we use for yield strength?If you had a Load (yaxis) vs Displacement (xaxis) curve, how do you calculate the yield strength?



Solved B Calculate The 0 2 Offset Yield Stress In Gpa Chegg Com


An Introductory Guide To Uniaxial Tensile Testing Stampingsimulation
The 02 Percent Offset Rule The most common engineering approximation for yield stress is the 02 percent offset rule To apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material σ = 0 0 0 2 × E \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×E3211 offset compressive yield strength—the stress at which the stressstrain curve departs from linearity by a specified percent of deformation (offset) 3212 percent compressive strain—the compressive deformation of a test specimen expressed as a percent of the original gage length 3213 proportional limit—the greatest stressProof stress is also known as offset stress because it is the stress required to make the material yield Corrosionpedia explains Proof Stress Proof stress is usually calculated for metals that do not have a properly defined yield strength For example, consider the stressstrain graph below for low carbon steel The graph has a distinct shape
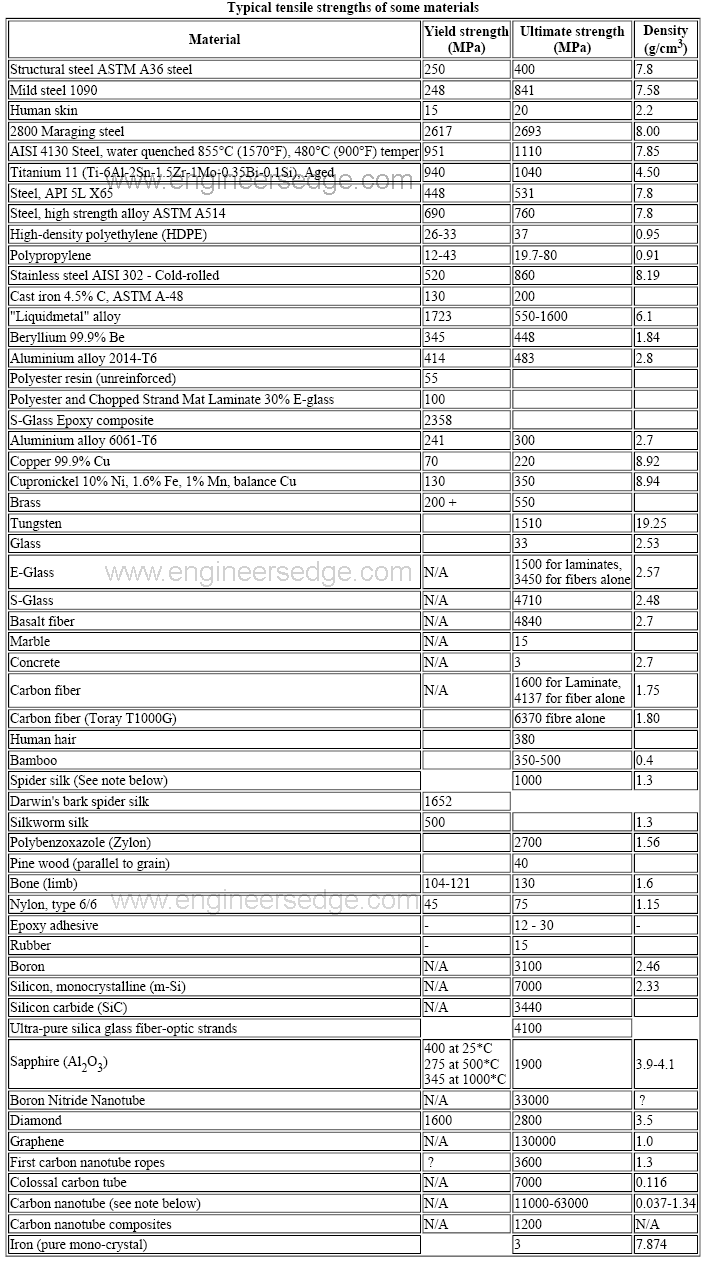


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Http Web Mit Edu Dlizardo Www Uniaxialtestinglabreportv6 Pdf
Hardening behavior and yield offset In the last form of the Ramberg–Osgood model, the hardening behavior of the material depends on the material constants and Due to the powerlaw relationship between stress and plastic strain, the Ramberg–Osgood model implies that plastic strain is present even for very low levels of stress Nevertheless, for low applied stresses and for the commonlyThe equation we want is simply (in this case) "* (x00)" (00 microinches/inch = 02% strain) For the from X value use 00 (or any smaller value);



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Civl 1101


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
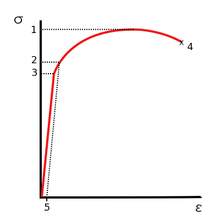


Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia


Q Tbn And9gcsubgeg9vwumror Qhoghyyxdjrgpugf4zei Gvjvgk9mt175y Usqp Cau
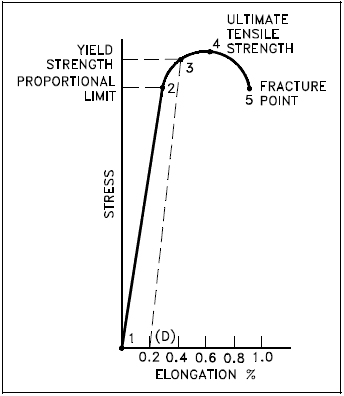


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University



Yield Strength


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve



Yield Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Astm E8 Measuring The Tensile Strength Of Metals
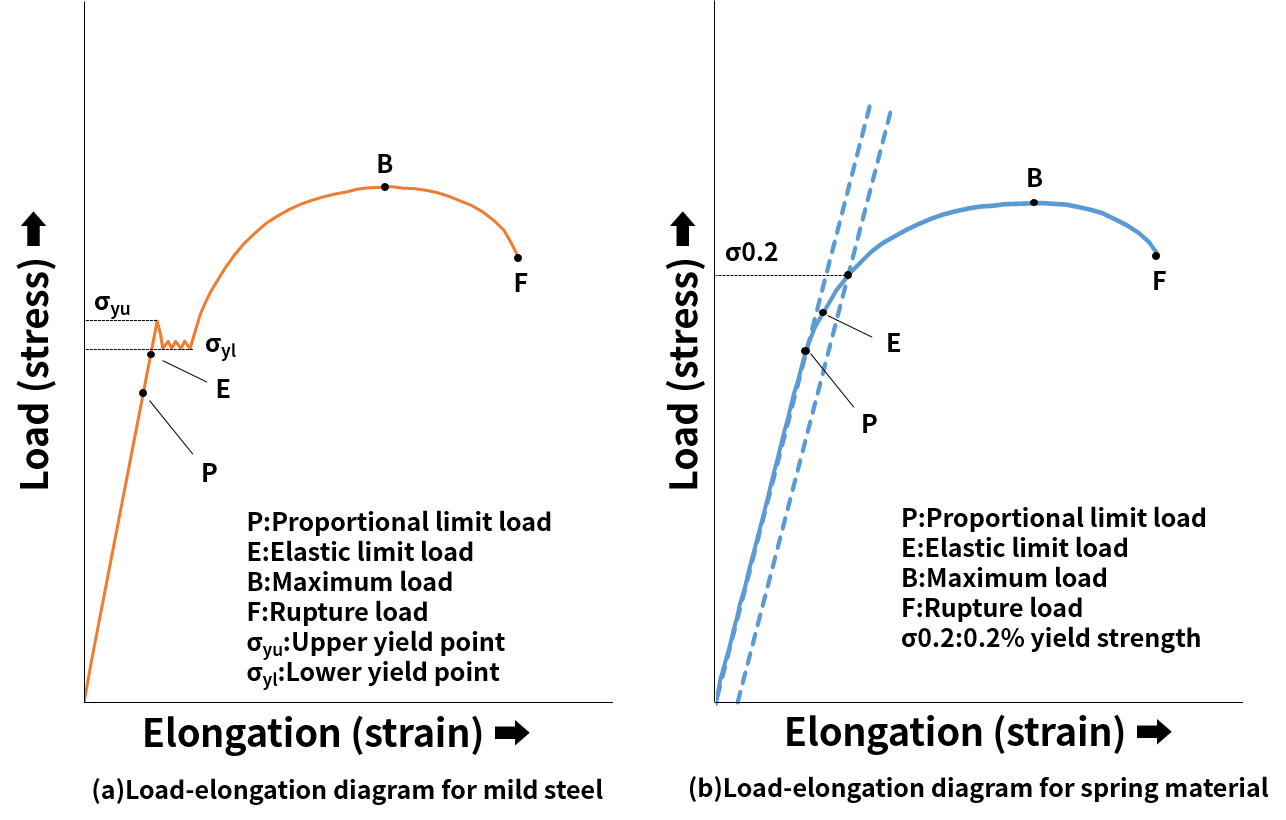


Compression Springs How To Calculate Spring Stress Tokai Spring Industries Inc
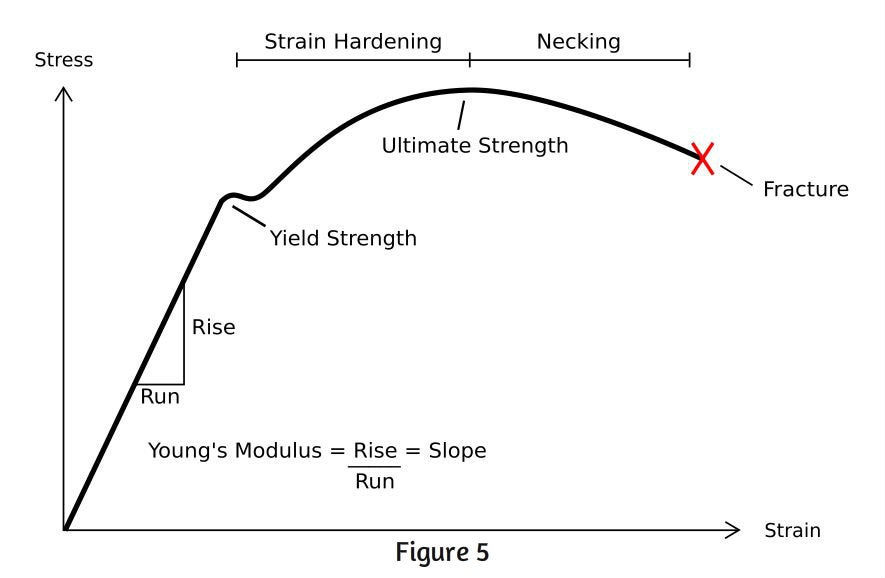


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables


Stress Versus Strain
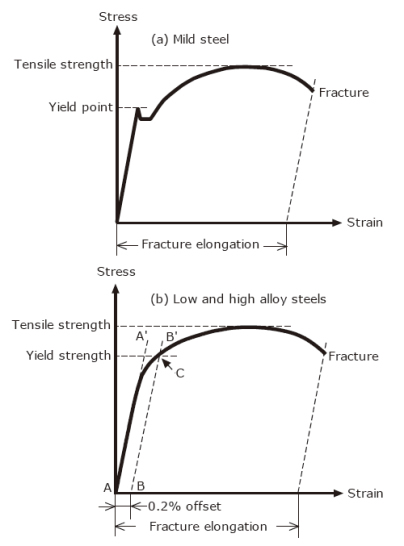


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd


Http Audi Nchu Edu Tw Wenjea Mechanical103 Chapter 3 Pdf
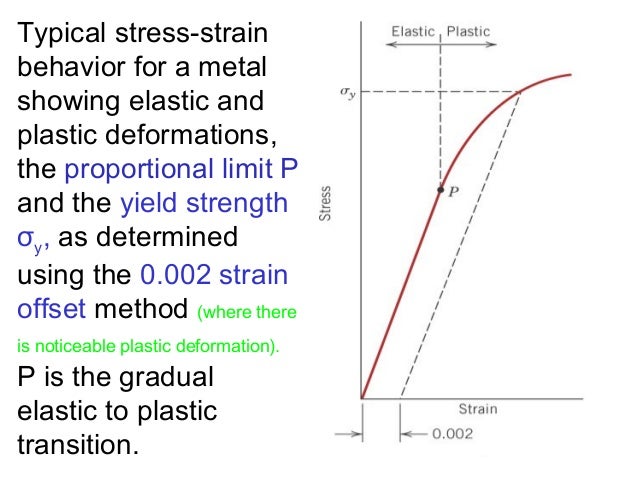


Mechanical Properties


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics



Calculate Yield Stress Youtube


Www Mdpi Com 76 3417 10 1 3 Pdf



Finding Minimum Difference Between Fit Line And Data Points In R Stack Overflow


People Engr Ncsu Edu Ytzhu Class Teaching Mse0 Lecture7 Sept16s Pdf



How To Draw A Line Parallel To The Linear Portion Of The Curve In Excel Stack Overflow



What Is Tensile Testing Instron



Strength At Break Tensile



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



On Cyclic Yield Strength In Definition Of Limits For Characterisation Of Fatigue And Creep Behaviour


Http Engin Swarthmore Edu Akrikor1 E6 labs E6lab2 Pdf


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


Q Tbn And9gcq Lokv6u6biweu7e6sd5mb7neolnaw Dcdbogfctf 8hvcdutp Usqp Cau


Q Tbn And9gcrhvogkniaf5aix Yv5viz777uqklm0zjg52gijgphwvl7khodo Usqp Cau



Yield Point Instron



Solved 3 19 The Stress Strain Diagram For A Bone Is Show Chegg Com



How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital


Mechanical Properties Of Metals I Ppt Download


Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 Bf Pdf


Www Acifoundation Org Portals 12 Files Pdfs Crc 81 Determination Of Yield Strength Pdf



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress



Mechanical Testing Tensile Testing Part 1 Twi



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University


Www Uotechnology Edu Iq Dep Electromechanic Typicall Lecture interface Lecture Pwr1 Eng Physics Pwr 6 Pdf


Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy


Http Maecourses Ucsd Edu Jmckittr Mae Wi11 Assignment 5 solutions Pdf


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic


Which Methods To Use For Sheet Metal Tension Testing


What Is 0 2 Of Offset Method In Yield Strength Quora
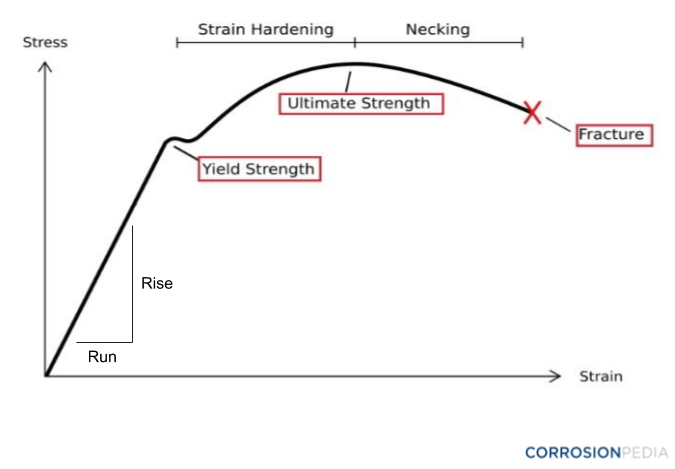


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia


Ocw Tudelft Nl Wp Content Uploads Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter6 Pdf
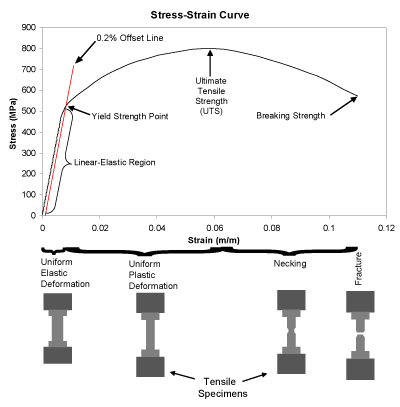


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Http Www Csun Edu Bavarian Courses Mse 527 Tension Test Mse 527l Pdf



On Cyclic Yield Strength In Definition Of Limits For Characterisation Of Fatigue And Creep Behaviour



How To Determine The Yield Strength Of Brass Quora
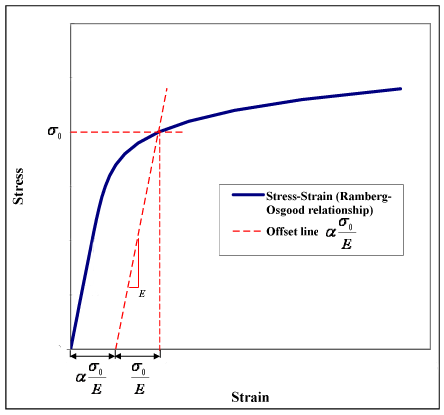


Ramberg Osgood Relationship Wikipedia
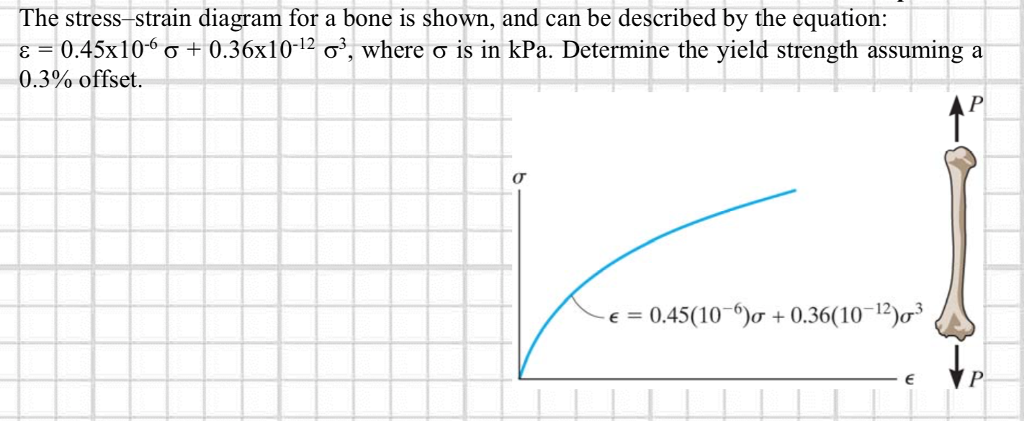


Solved The Stress Strain Diagram For A Bone Is Shown And Chegg Com



How To Draw A Line Parallel To The Linear Portion Of The Curve In Excel Stack Overflow


Why Do We Use 0 2 Offset In Aluminum Stress Strain Curve Quora



What Is 0 2 Of Offset Method In Yield Strength Quora


Http Www Schooloftesting Com Download How To Interpret Stress Strain Diagrams How to interpret stress Strain diagrams Pdf
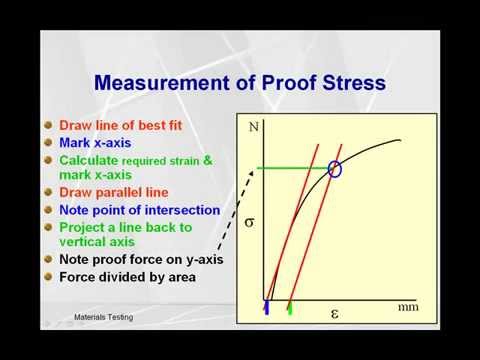


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube
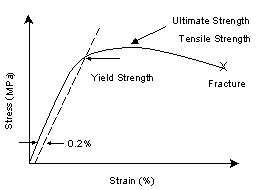


Efatigue Glossary Ultimate Strength



How To Find Yield Strength Quora


Http Web Ncyu Edu Tw Lanjc Lesson C3 Class Chap02 A Pdf



Solved Problem 1 Find The Ultimate Tensile Strength An Chegg Com



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau
コメント
コメントを投稿